How to Lead Design Thinking When People Aren’t Familiar with It?
Harvard Business Review 2019: How to Lead Design Thinking When People Aren’t Familiar with It?
Why Strong Leadership Is Crucial
Even more than other change-management processes, design thinking requires active and effective leadership to keep efforts on a path to success.
How?
By leveraging empathy, encouraging divergence and navigating ambiguity, and rehearsing new futures. #commercialinnovation #servicedesign
The importance of customer centricity and customer experience in B2B
B2B companies will also need to shift to a customer-centered business model
Three Driving Forces in B2B Markets
Consumerization of customer expectations
Distinct characteristics of B2B purchasing
Evolving analytics and algorithms
Four Pillars of Superior Digital Customer Experience
Pillar 1: Comprehensive, Personalized Customer Experiences
Pillar 2: Segmented Customer Needs
Pillar 3: Facilitated Customer Interactions
Pillar 4: Customer-Centered Operating Models
[Service design] - What makes a customer really happy?
What makes a customer really happy?
Nowadays, [value propositions], [segmentation] and [market approaches] based on [customer / buyer journeys and personae], are an integral part of modern commercial policy. But is this enough to make a [competitive difference]?
Read more
Listen to customers
An easy but very powerful key question in commercial innovation. What you really want to know about your (potential)customers…
What makes a customer really happy?
[Commercial innovation] Happy Customers
Nowadays, value propositions, segmentation and market approaches based on customer / buyer journeys and personae, are an integral part of modern commercial policy. But is this enough to make a competitive difference?
Sometimes companies forget to focus on the main DRIVER and main reason for commercial innovation initiatives. ‘What makes a customer really happy?’ is the underlying core question to gain in-depth insights into the customer's needs and wishes, their motives and emotional involvement, from the development of new services, from their commercialization, and from the daily realization of these services.
In summary, we can say that it is the personal context related to the the underlying question of what makes a customer really happy, that is more determining than only the technical writing of personae, journeys and value propositions.
If we are able to develop an 'iterative approach' to be in permanent contact with customers and prospects, to understand their real (emotional) challenges, to relate their personal context to our solutions and innovations, to transfer it optimally to the daily operational activities, then we create added value. ‘What makes the customer really happy?”, is the core question that every employee should ask him-/herself permanently.
Developing new services, products or even new customer approaches, without a clear answer to this key core question doesn't solve anything. In many companies, marketing teams, design teams and R & D teams are working on the (commercial) innovations of the future, but at a great distance from the end user / customer.
Therefore these 5 tips
Learn from ‘them’, co-create and test together
Learn about 'them': learn and experience the customer in real life and their personal context, and not only from desk research. Test and co-create with customers at all stages of innovation and even during the roll out. Learn about the actual impact of competition on your customers and prospects.
Involve marketing and sales from the start: they know the customers in a different way and have access to them. By involving them actively from the start, it will become also easier for them to sell or market these new services and products afterwards. They will better understand what the added value for the customer will be.
Involve marketing and sales from the beginning
In-depth interviews
Create a system of Learning Cycles: make use of short learning cycles with internal and external customers as important test. Adjust quickly in the learning process after interaction with and feedback of the customers. Build, measure, learn, build further!
Quality of ideas * execution = value
Understand happiness: learn how to work with in-depth interviews, panels or focus groups in all phases of the development / commercial innovation. Go to the bottom to understand in detail what 'Happy' really means and how this can be reached during the customer journey towards happiness.
Learning cycles
Don't forget
'The Quality of ideas * Execution = Value' The world’s simplest formula… explains why you can’t forget commercialization. Develop and test therefore The Most Valuable Commercial Approach.
How does service design work?
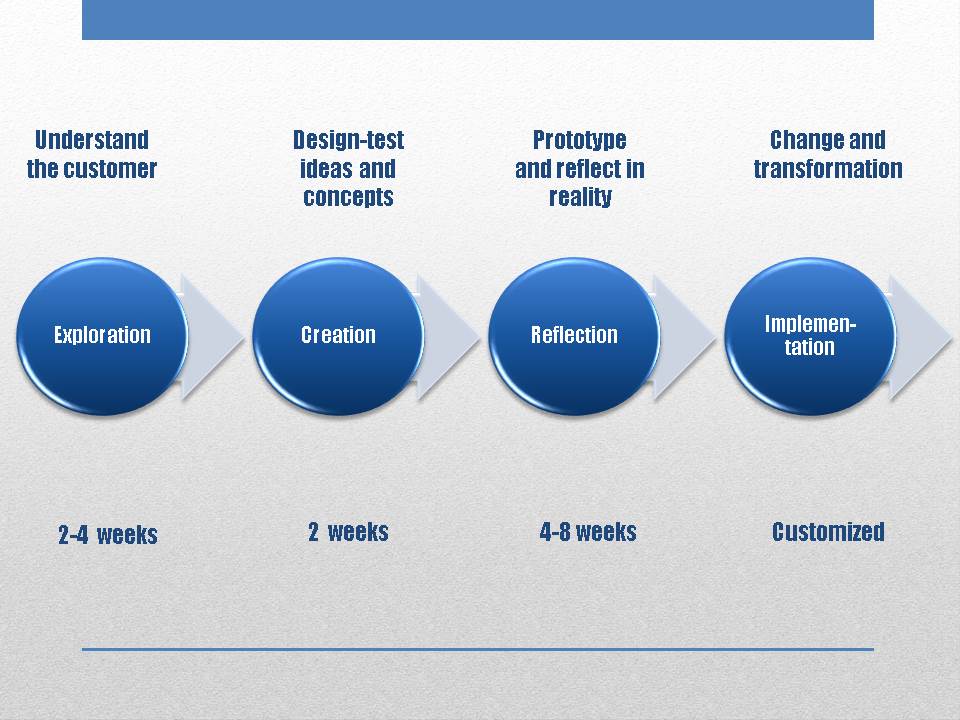
Service design is an iterative process in four steps.
The basic service design approach consists of exploration, creation, reflection, and implementation.
Service design
Is an iterative process in four steps
Fundamentally and in reality, it is not a linear process and certainly not a standard process. But as service design is a complex process, we work in four different steps to structure the approach. The basic service design approach consists of exploration, creation, reflection, and implementation.
It is also an iterative process. That means that it must be able to return to the previous step regularly, or even start all over again from scratch. It is necessary to be critical and courageous to step back, start all over again, or even stop the design process. The benefit of structuring the design process is that it enables a greater degree of reflection upon all activities, outcomes and influences of the design team.
Keep always the entire process in mind (from a helicopter view), especially when you put a lot of energy in the improvement of a concrete activity with lots of details. E.g. if you are redesigning employee interactions between sales and marketing staff, it is also important to consider the organizational level and structure as a whole. In other words, it is not a success to work on interactions between two people respectively from the marketing and sales department, as these departments themselves need to improve cooperation and interaction.
Four steps
The starting point in the exploration phase is the customer. Whether it is for current customers or potential customers, it is essential to properly understand the situations, interactions, customer journeys, attitudes and expectations of the (potential) customers. Ways of researching are for example by going on an exploratory manner in conversation with the customer, customer panels, or by observing customers. The ways in which this information is obtained, and the attention to details are keys to future success.
During the creation stage, it is all about designing, testing and retesting ideas and concepts. It is a co-creative ideation process, where it is important to involve all main stakeholders and to work with interdisciplinary teams that include customers, managers, employees, engineers, designers, sales, marketing and other stakeholders. In this stage it is important to stimulate co-creativity as much as possible, and to work user-centred. Using sticky notes for visualizing the process is another key to success. The creation stage is closely related to the reflection stage. Practically, there are a variety of methods and tools which can be used in the creation stage. E.g. designing hypothetical stories, drawing storyboards (sequence of events), or even using Lego materials to express a service environment ,can all be interesting to use during the creation stage.
As already told, the reflection stage is closely related to the creation stage. However, in the reflection stage it is important to build or prototype service concepts in reality or circumstances close to reality. But the main challenge at this stage in the process is dealing with the intangibility of services. Therefore it will be very helpful to consider carefully how to provide customers with a good mental image about the future service. That is the main goal at this stage. In order to obtain emotional engagement for the new service, the way in which this is proposed will be of great importance. Methods which are useful for this purpose and help visualize the new service are again methods like storyboards, a comic strip, video, photos, simulations and co-creation. Feedback needs to be collected in a thorough way through interviews, observation, surveys.
A design process is not successful, if the new service isn’t implemented properly. The implementation stage may be considered as a real change or transformation stage, with lots of obstacles and resistances. Therefore it is very important to work with ‘ambassadors’, who were already involved and contributed already in earlier stages. If they have a clear vision of the concept, and if they were already involved in developing and testing the prototype of the new service in interaction with real customers, there is a high probability of a successful implementation. Successful methods we use in this stage are storytelling, service blueprints, testing with real customers or role plays, business model canvas and action plans.
In every stage we have several workshops with main stakeholders, but with different goals, perspectives and approaches.
If you want more information about service design thinking and to evaluate if this approach could be interesting for your organization, contact THRUST
For more information about our services, click here


![[Service design] - What makes a customer really happy?](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/56f53cf6b09f955f052e3847/1588082493343-TO1H22CSB6ODQUUVTLN6/Canva+-+Closeup+Photo+of+Gray+and+Black+Custom+Frame.jpg)

![[Commercial innovation] Happy Customers](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/56f53cf6b09f955f052e3847/1588073257358-OWJDUX6VWUIWGMWPAFUU/%5Bcommercial+innovation%5D+Happy+customers.jpg)